Biocaxis > Products > Nucleotide |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
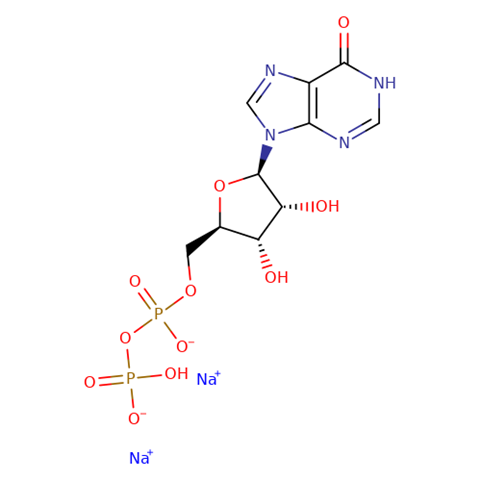 Inosine-5'-diphosphate disodium
Inosine-5'-diphosphate disodium
Catalog NO.: NDP-010 | CAS NO.: 54735-61-4 | Brand: BIOCAXIS
Category
Nucleosides & Nucleotides, Nucleotide
Synonyms
IDP disodium salt, Disodium 5′-IDP,
Disodium Inosine 5′-diphosphate, 5′-IDP-Na2;
Inosine-5'-diphosphoric acid disodium salt
Molecular Formula
Molecular Weight
472.15
General description
Inosine-5'-diphosphate disodium salt (IDPS) is a nitro
compound that is used in the synthesis of antibacterial drugs. It is also used
in the production of polymers and as a precursor to other organic compounds.
IDPS has been shown to have antibacterial activity against halogeno
bacteria, such as buprestidae, and many Gram-positive
bacteria, including encapsulated strains. IDPS has been shown to be effective
against both damaged cells and healthy cells in culture. The mechanism of
action may involve inhibition of protein synthesis by blocking the ribosomes or
by interfering with DNA replication. This drug also inhibits growth rate of
japonica rice and heterocycles.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Uridine 5′-diphosphate (UDP)
is an endogenous signaling molecule produced by damaged cells to attract
macrophages. In response to neuronal damage, UDP promotes chemotaxis and chemokinesis in microglial cells.[3] UDP serves as a ligand
for P2Y receptors. UDP and uridine 5′-triphosphate
(UTP) may be used in studies on nucleic acid (RNA) biosynthesis and cell
signaling. UDP is a nucleotide that upon phosphorylation to UTP becomes a
substrate for enzymes such as RNA polymerase(s) and GTPases. These enzymes are
involved in a wide range of applications from the synthesis of RNA to the
regulation of G-coupled protein receptors (GPCR) and cell signaling molecules
such as Rho-signaling via guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF).

