Biocaxis > Products > Purine &
Pyrimidine |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
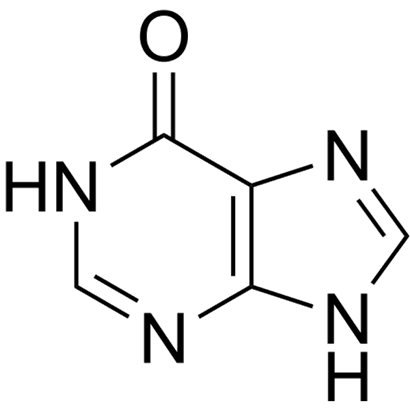 Hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine
Catalog NO.: BASE-003
| CAS NO.: 68-94-0 |
Brand: BIOCAXIS
Category
Nucleosides & Nucleotides, nucleobase
Synonyms:
1,9-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-one; 3H-Purin-6-ol;
6-Hydroxy-1H-purine; 6-Hydroxypurine; 6-Oxopurine; Hypoxanthine enol; NSC
129419; NSC 14665; Purin-6-ol; Sarcine; Sarkin; Sarkine; USP Didanosine Related
Compound A; 7H-Purin-6-ol; 1,7-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-one
Molecular Formula
C5H4N4O
Molecular Weight
136.11
General description
Hypoxanthine, a purine derivative, is a potential free
radical generator and could be used as an indicator of hypoxia.
Hypoxanthine (6-hydroxypurine), a purine derivative is a
naturally occurring compound. It is the deaminated form of adenine and a
breakdown product of adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
Application
Hypoxanthine is a nutrient additive for a variety of cell
culture applications involving bacterial, parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) and
animal cells. Hypoxanthine is a component of selection media used in hybridoma
technologies.
Hypoxanthine has been used:
as a supplement in HEPES
(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) -buffered Roswell park
memorial institute (RPMI) to culture Plasmodium falciparum strain IT/FCR3
in the preparation of Dulbecco′s modified eagle′s
medium (DMEM) + MXH for the selection of chimeric modified vaccinia virus ankara (MVA)
to generate superoxide anions
to prepare hybridoma selection and maintenance media.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Hypoxanthine is capable of stimulating cell death. It can
also induce reactive oxygen species (ROS). It results in endothelial
dysfunction via apoptosis, stimulated by oxidative stress.
http://www.biocaxis.com

