Biocaxis > Products > Nucleoside |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
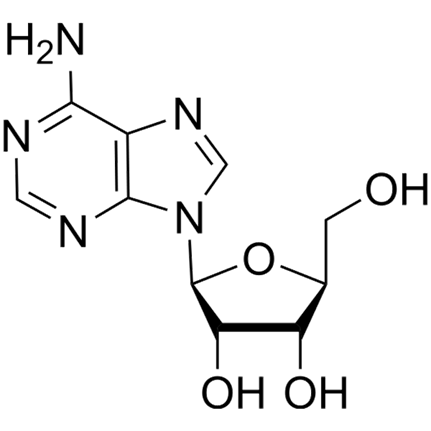 L-Adenosine
L-Adenosine
Catalog NO.: L-NS-001
| CAS NO.: 3080-29-3 |
Brand: BIOCAXIS
Category
Nucleosides & Nucleotides, L-nucleoside
Synonyms:
9-(b-L-Ribofuranosyl)adenine
Molecular Formula
C10H13N5O4
Molecular Weight
267.24
General description
L-Adenosine is a nucleoside that is naturally synthesized
in the body and is also found in certain foods. It has a variety of functions,
including as an adenosine receptor agonist, a transport agent, and a substrate
for metabolic pathways. In addition to its function as an adenosine receptor
agonist, L-adenosine can be transported into mammalian cells by facilitated
diffusion. The uptake of L-adenosine into cells is dependent on the
concentration of extracellular adenosine and its concentration-response curve
has been determined experimentally. L-Adenosine also acts as an inhibitor of
phosphodiesterase enzyme which increases cAMP levels in cells. This increase in
cAMP leads to increased calcium ion influx into the cell, which may lead to
activation of protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC). L-Adenosine has
been shown to have cardiac effects at high concentrations.
L-Adenosine, a naturally occurring nucleoside found in
living organisms, comprises adenine and the sugar ribose. This purine
nucleoside plays a role in numerous vital cellular processes, including energy
metabolism, signal transduction, and gene regulation. Moreover, it serves as a
fundamental constituent of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell′s
principal energy currency. L-Adenosine assumes significant importance in
comprehending cellular mechanisms and has been extensively investigated in
laboratory applications. Its utility spans a wide range of research areas, such
as gene regulation, signal transduction, and cell metabolism. Furthermore,
L-Adenosine finds application in the examination of drug effects on cellular
processes, the study of radiation′s impact on cells, and the exploration
of various environmental factors, including temperature and pH, on cellular
activities.
L-Adenosine is a metabolically stable enantiomeric analog
and also is a potential probe. L-Adenosine has weakly inhibitory adenosine deaminase (ADA) activity with
an Ki value of 385 μM.
L-Adenosine can be used for the research of adenosine uptake and accumulation.

